Most Spring Tutorials available online teach you how to create/secure a Rest API with Spring boot. However, sometimes there will be specific use cases where you will need to create/secure REST API without using spring boot. This tutorial aims to help you create a REST application without using Spring Boot at all.
Note: If you don’t wanna use even the Spring framework, then you can read on how to create REST API in Java without Spring.
What you’ll build
A Spring REST service which will simply accept a name as a path variable in the request and say hello with that name in the response

What you’ll need
- Spring Tool Suite 4
- JDK 11
- MySQL Server 8
- Maven
Tech Stack
- Spring 5
- JDK 11
- Log4j 2
Bootstrap your application
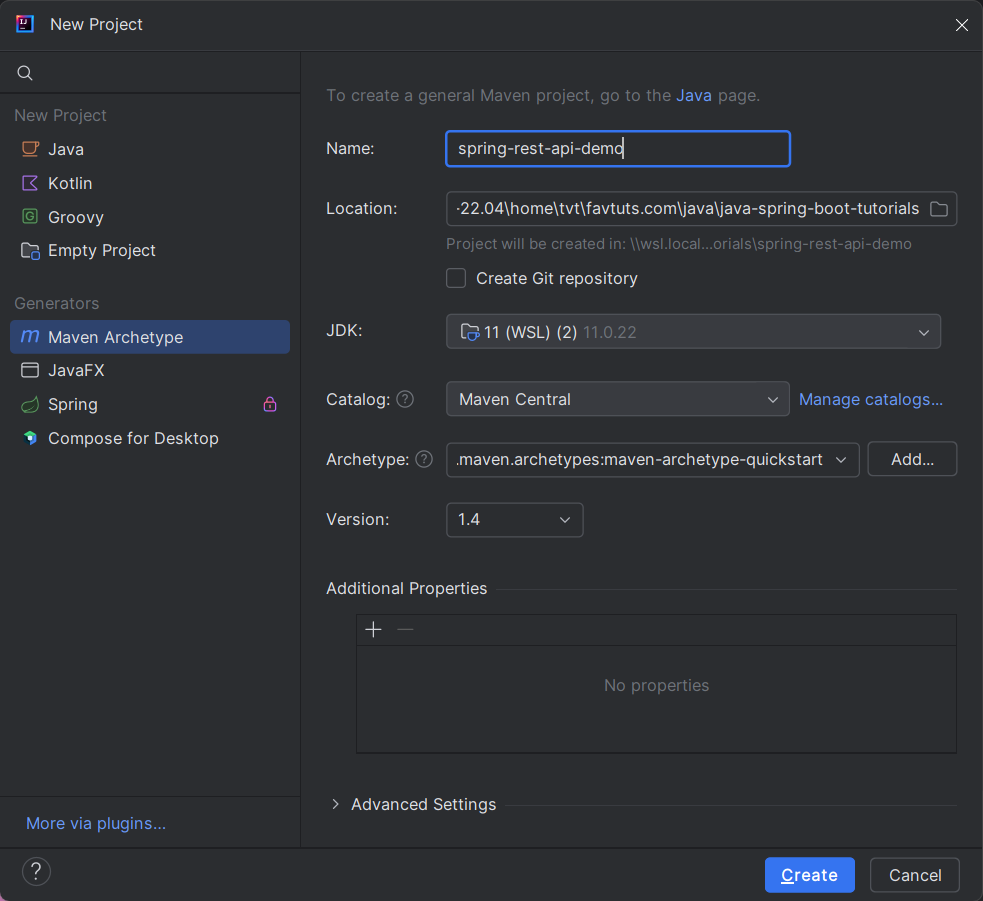
Let’s bootstrap the application by creating a maven project in STS or IntelliJ IDEA
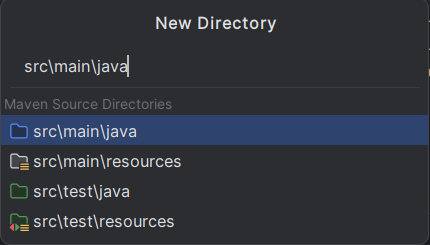
Then create directories (src/main/java and src/main/resources)
Project Dependencies
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.favtuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rest-api-demo</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-rest-api-demo Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<java-version>11</java-version>
<spring.version>5.2.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
<hibernate.version>5.4.1.Final</hibernate.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Web MVC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Required for converting JSON data to Java object and vice versa -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.10.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringRestApiDemo</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java-version}</source>
<target>${java-version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<warName>SpringRestJwt</warName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>Spring Configuration
SpringWebInitializer.java
WebApplicationContext can be configured using web.xml or Java-based configuration as shown below
SpringWebInitializer class extends Spring’s AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer to configure the WebApplicationContext.
package com.javachinna.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class SpringWebInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {};
}
}WebConfig.java
WebConfig class implements WebMvcConfigurer to configure the Jackson message converters
@EnableWebMvc annotation is used to enable Spring MVC support
@ComponentScan annotation is used with the @Configuration annotation to tell Spring the packages to scan for annotated components.
package com.javachinna.config;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.javachinna")
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter());
}
}Create REST Controller
GreetController.java
Controller class for exposing a GET REST API
package com.javachinna.controller;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class GreetController {
private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(GreetController.class);
@GetMapping("/greet/{name}")
public String greet(@PathVariable String name, ModelMap model) {
String greet = "Hello!!! " + name + " How are You?";
logger.info(greet);
return greet;
}
}Log4J Configuration
log4j.properties
# Root logger option
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout, file
# Redirect log messages to console
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
# Redirect log messages to a log file
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
#outputs to Tomcat home
log4j.appender.file.File=${catalina.home}/logs/myapp.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=5MB
log4j.appender.file.MaxBackupIndex=10
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%nBuild Application
Run mvn clean install command to clean and build the war file
Deploy Application
Deploy the generated war file in a server like tomcat and hit the URL http://localhost:8080/SpringRestJwt/greet/Chinna
Conclusion
That’s all folks. In this article, we have developed a simple Spring REST service without using Spring Boot. Thank you for reading