In this blog, I have discussed an overview of Azure traffic manager and its different types of traffic-routing methods. I have also covered features of Azure traffic manager and practical demonstration on a traffic manager profile.
Azure Traffic Manager is a global DNS Server hosted in Azure. It is an external DNS solution. It extends the functionality of DNS beyond simple name, IP resolution by adding load balancing and advance features such as geo-fencing, weighted, performance name resolutions. I have discussed all in detail below
1. What Is Azure Traffic Manager?
Azure Traffic Manager allows you to regulate the distribution of user traffic by using DNS to direct requests to the most appropriate service endpoint supported on a traffic-routing method and therefore the health of the endpoints.
Azure traffic manager selects an endpoint based on the configured routing method. It supports a variety of traffic-routing methods to suit different application needs. After the selection of endpoints, the client is connected directly to the appropriate service point. It also provides endpoint health checks and automatic failover. It also enables you to build a highly available application that is resilient to failure, including the failure of an entire Azure region.

2. Why Do We Use Traffic Manager?
Traffic Manager uses DNS to direct client requests to the most appropriate service endpoint based on a traffic-routing method and the health of the endpoints. An endpoint is any Internet-facing service hosted inside or outside of Azure. It provides a range of traffic-routing methods and endpoint monitoring options to suit different application needs and automatic failover models. It is resilient to failure, including the failure of an entire Azure region.
3. Azure Traffic Manager Routing Methods
Azure Traffic Manager distributes the traffic based on one of the six traffic-routing methods that determine which endpoint is returned within the DNS response.
These following traffic routing methods which are available:
1.) Priority
When you select the priority routing method, it contains a prioritized list of service endpoints where the primary service endpoint has the highest priority for all traffic. If the primary service endpoint is unavailable, it redirects the traffic to the second priority endpoint and so on.

2.) Weighted

The weighted routing method is used when you want to distribute traffic evenly or to use pre-defined weightsacross a set of endpoints. In this traffic-routing method, you allocate a weight which is an integer from 1 to 1000, to each endpoint in the Microsoft Azure Traffic Manager profile configuration.
3.) Performance

This traffic routing method is used when you want to improve the responsiveness of many applications by routing traffic to the location that is closest to the user. The ‘closest’ endpoint isn’t necessarily closest as measured by geographic distance. Instead, the ‘Performance’ traffic-routing method determines the closest endpoint by measuring network latency.
Check Out: Our previous blog post on Azure Automate Deployement.
4.) Geographic

In Geographic routing, each endpoint associated with that profile must have a set of geographic regions assigned thereto. When a region or a set of regions is assigned to an endpoint, any requests from those regions get routed only thereto endpoint.
5.) Multivalue
You can select MultiValue for Azure Traffic Manager profiles which may only have IPv4/IPv6 addresses as endpoints. When a question is received for this profile, all healthy endpoints are returned.
6.) Subnet
Select the Subnet traffic-routing method to map sets of end-user IP address ranges to a specific endpoint within an Azure Traffic Manager profile. When a request is received, the endpoint returned are getting to be the one mapped for that request’s source IP address.
4. Features Of Azure Traffic Manager
Some of the features are discussed below:
1) Increase application availability
It provides high availability for your critical applications by monitoring your endpoints and delivering automatic failover when an endpoint goes down.
2) Improve application performance
Azure allows you to run cloud services or websites in data centres located all over the world. It enhances application responsiveness by directing traffic to the endpoint with the lowest network latency for the client.
3) Perform service maintenance without downtime
You can perform planned maintenance operations on your applications without downtime. It can direct traffic to alternative endpoints while the unkeep is ongoing.
4) Combine hybrid applications
Microsoft Azure Traffic Manager supports external, non-Azure endpoints enabling it to be used with hybrid cloud and on-premises deployments, including the “burst-to-cloud”, “migrate-to-cloud,” and “failover-to-cloud” scenarios.
5) Distribute traffic for complex deployments
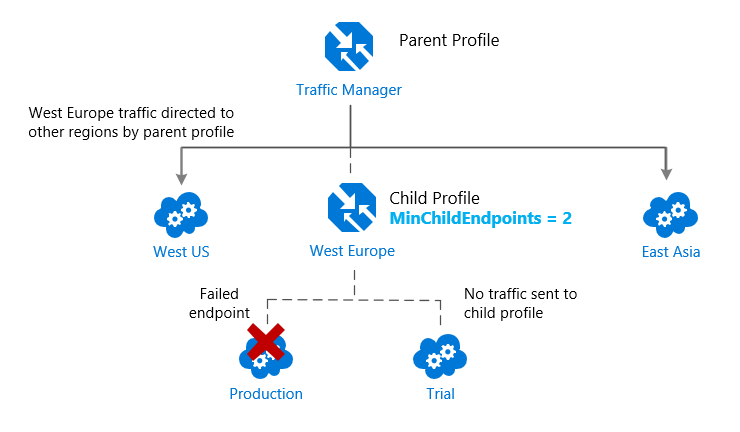
Using nested Azure Traffic Manager profiles, multiple traffic-routing methods are often combined to make sophisticated and versatile rules to scale to the requirements of larger, more complex deployments.
5. Hands-on Of Traffic Manager Profile
Step 1) Log in to Azure Portal (Please make sure you have a subscription before doing all this. If you created a free account for the first time, you’ll already have a FREE TRIAL subscription for 1 month).
NOTE: For this quickstart, you’ll need two instances of a web application deployed in two different Azure regions (East US and Central US). Each will serve as primary and failover endpoints for Traffic Manager
If you don’t know how to create an instance or virtual machine then click on Create a Virtual Machine to know more

Create a Traffic Manager profile that directs user traffic based on endpoint priority
Step 2) On the upper-left side of the screen, select Create a resource > Networking > Traffic Manager profile.

Check Out: What is ARM Template in Azure.
Step 3) In the Create Traffic Manager profile, enter, or select these settings
Name: Enter a unique name for your Traffic Manager profile.
- Routing method: Select Priority.
- Subscription: Select the subscription you want the traffic manager profile applied to.
- Resource group: Select your existing Resource Group or Create new
- Location: This setting refers to the location of the resource group. It has no effect on the Traffic Manager profile that will be deployed globally.

Step 4) Select Create and its done now you have created successfully traffic manager profile on Azure
Conclusion: The azure traffic manager is an external DNS that is used to distribute user traffic, its routing methods help to distribute traffic in an effective way that determines which endpoint is returned within the DNS response. The practical Hands-on helps you to understand concepts in more detail.