Few Java examples to declare, initialize and manipulate Array in Java
1. Declares Array
1.1 For primitive types.
ArrayExample1.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
declareArrayPrimitiveTypes();
}
static void declareArrayPrimitiveTypes() {
//declares an array of integers
int[] num1 = new int[5];
int[] num2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] num3 = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// index starts with 0
num1[0] = 1;
num1[1] = 2;
num1[2] = 3;
num1[3] = 4;
num1[4] = 5;
// print array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num2));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num3));
}
}
Output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]1.2 For classes or objects, like String.class, it’s the same.
ArrayExample1.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
declareArrayClassesObjects();
}
static void declareArrayClassesObjects() {
String[] str1 = new String[5];
String[] str2 = {"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
String[] str3 = new String[]{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
str1[0] = "a";
str1[1] = "b";
str1[2] = "c";
str1[3] = "d";
str1[4] = "e";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str2));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str3));
}
}
Output
[a, b, c, d, e]
[a, b, c, d, e]
[a, b, c, d, e]2. Return Array
2.1 A method to return an Array.
ArrayExample2.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
declareArrayFromMethodReturn();
}
static void declareArrayFromMethodReturn() {
int[] resultNum = getArrayNumber();
String[] resultStr = getArrayString();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(resultNum));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(resultStr));
}
public static int[] getArrayNumber() {
return new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
}
public static String[] getArrayString() {
return new String[]{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
}
}
Output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[a, b, c, d, e]3. Access Array
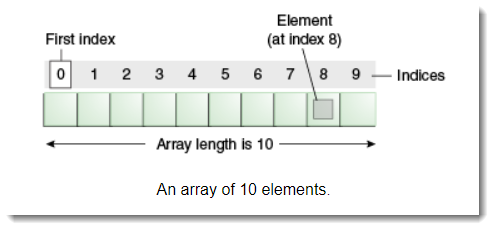
3.1 Array index starts with 0
ArrayExample3.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
accessArrayWithIndexStartsWith0();
}
static void accessArrayWithIndexStartsWith0() {
// array, empty
int[] num;
// array of 5 elements
num = new int[5];
num[0] = 1;
num[1] = 2;
num[2] = 3;
num[3] = 4;
num[4] = 5;
System.out.println("num[0] : " + num[0]);
System.out.println("num[1] : " + num[1]);
System.out.println("num[2] : " + num[2]);
System.out.println("num[3] : " + num[3]);
System.out.println("num[4] : " + num[4]);
}
}
Output
num[0] : 1
num[1] : 2
num[2] : 3
num[3] : 4
num[4] : 54. ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
4.1 If accessing with an index greater than the size of an array. Again, the index starts with 0.
ArrayExample4.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
accessArrayOutOfBoundsException();
}
static void accessArrayOutOfBoundsException() {
// array, empty
int[] num;
// array of 5
num = new int[5];
num[0] = 1;
num[1] = 2;
num[2] = 3;
num[3] = 4;
num[4] = 5;
//num[5] = 6; //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
System.out.println("num[0] : " + num[0]);
System.out.println("num[1] : " + num[1]);
System.out.println("num[2] : " + num[2]);
System.out.println("num[3] : " + num[3]);
System.out.println("num[4] : " + num[4]);
System.out.println("num[5] : " + num[5]); //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
}
}
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
at com.favtuts.array.InitArray.accessArrayOutOfBoundsException(InitArray.java:36)
at com.favtuts.array.InitArray.main(InitArray.java:13)5. Multidimensional Array
ArrayExample5.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
declareMutidimensionalArray();
}
static void declareMutidimensionalArray() {
int[][] num2d = new int[2][5];
num2d[0][0] = 1;
num2d[0][1] = 2;
num2d[0][2] = 3;
num2d[0][3] = 4;
num2d[0][4] = 5;
num2d[1][0] = 10;
num2d[1][1] = 20;
num2d[1][2] = 30;
num2d[1][3] = 40;
num2d[1][4] = 50;
//or like this :
int[][] num2dInit = {
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
};
// Accessing 2d array with index print
int index1d, index2d = 0;
for (int[] num1d : num2d) {
index1d = 0;
for (int num : num1d) {
System.out.println("[" + index2d + "][" + index1d + "] = " + num);
index1d++;
}
index2d++;
}
/* Simple print
for (int[] num1d : num2d) {
for (int num : num1d) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}*/
}
}
Output
[0][0] = 1
[0][1] = 2
[0][2] = 3
[0][3] = 4
[0][4] = 5
[1][0] = 10
[1][1] = 20
[1][2] = 30
[1][3] = 40
[1][4] = 506. Copy Array
We can use System.arraycopy to copy data from an Array into another.
arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);ArrayExample6.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
copyDataFromArrayToAnother();
}
static void copyDataFromArrayToAnother() {
int[] arrayFrom = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int[] arrayTo = new int[5];
int[] arrayTo2 = new int[10];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayFrom));
//[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
System.arraycopy(arrayFrom, 2, arrayTo, 0, 5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayTo));
//[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
System.arraycopy(arrayFrom, 0, arrayTo2, 5, 5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayTo2));
}
}
Output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Read Java docs System.arraycopy
7. Sort Array
We can use Arrays.sort to sort an Array.
ArrayExample7.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
initArrayThenSortArray();
}
static void initArrayThenSortArray() {
int[] num = {10, 5, 4, 3, 6, 9, 7, 8, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
// ascending order
Arrays.sort(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
// descending order, int[] cant, need boxed to Integer[] first
Integer[] numObjects = Arrays.stream(num).boxed().toArray(Integer[]::new);
Arrays.sort(numObjects, Collections.reverseOrder());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numObjects));
}
}
Output
[10, 5, 4, 3, 6, 9, 7, 8, 2, 1]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]8. Join Array
We can use Stream to join multiple Arrays.
ArrayExample8.java
package com.favtuts.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class InitArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
createArrayByJoiningArrays();
}
static void createArrayByJoiningArrays() {
String[] s1 = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
String[] s2 = new String[]{"d", "e", "f"};
String[] result = Stream.of(s1, s2).flatMap(Stream::of).toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
int[] num1 = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
int[] num2 = new int[]{4, 5, 6};
int[] result2 = IntStream.concat(Arrays.stream(num1), Arrays.stream(num2)).toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result2));
}
}
Output
[a, b, c, d, e, f]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]9. FAQs
Download Source Code
$ git clone https://github.com/favtuts/java-core-tutorials-examples
$ cd java-basic/array