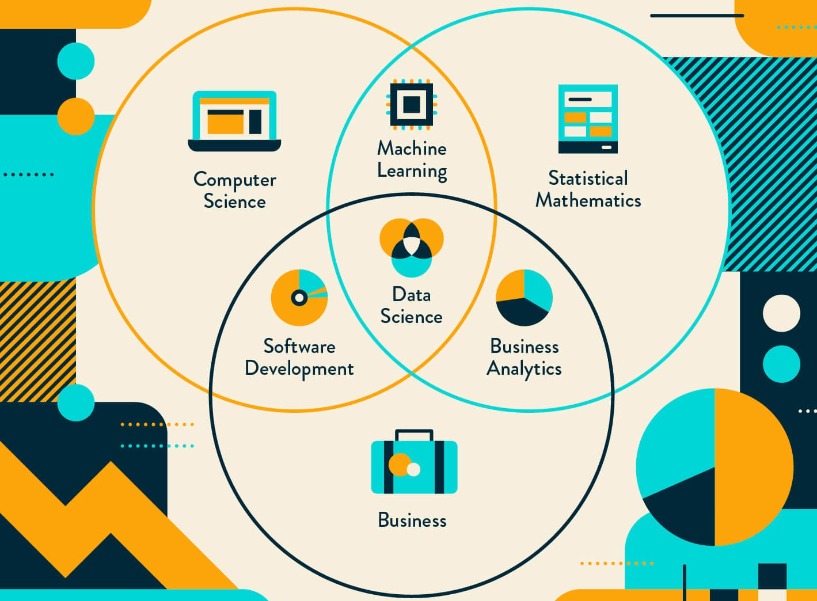
Data science is an essential part of many industries today, given the massive amounts of data that are produced, and is one of the most debated topics in IT circles. Its popularity has grown over the years, and companies have started implementing data science techniques to grow their business and increase customer satisfaction. In this article, we’ll learn what data science is, and how you can become a data scientist.
What Is Data Science?
Data science is the domain of study that deals with vast volumes of data using modern tools and techniques to find unseen patterns, derive meaningful information, and make business decisions. Data science uses complex machine learning algorithms to build predictive models.
The data used for analysis can come from many different sources and presented in various formats.
Now that you know what data science is, let’s see why data science is essential to today’s IT landscape.
The Data Science Lifecycle
Data science’s lifecycle consists of five distinct stages, each with its own tasks:
- Capture: Data Acquisition, Data Entry, Signal Reception, Data Extraction. This stage involves gathering raw structured and unstructured data.
- Maintain: Data Warehousing, Data Cleansing, Data Staging, Data Processing, Data Architecture. This stage covers taking the raw data and putting it in a form that can be used.
- Process: Data Mining, Clustering/Classification, Data Modeling, Data Summarization. Data scientists take the prepared data and examine its patterns, ranges, and biases to determine how useful it will be in predictive analysis.
- Analyze: Exploratory/Confirmatory, Predictive Analysis, Regression, Text Mining, Qualitative Analysis. Here is the real meat of the lifecycle. This stage involves performing the various analyses on the data.
- Communicate: Data Reporting, Data Visualization, Business Intelligence, Decision Making. In this final step, analysts prepare the analyses in easily readable forms such as charts, graphs, and reports.
Prerequisites for Data Science
Here are some of the technical concepts you should know about before starting to learn what is data science.
1. Machine Learning
Machine learning is the backbone of data science. Data Scientists need to have a solid grasp of ML in addition to basic knowledge of statistics.
2. Modeling
Mathematical models enable you to make quick calculations and predictions based on what you already know about the data. Modeling is also a part of Machine Learning and involves identifying which algorithm is the most suitable to solve a given problem and how to train these models.
3. Statistics
Statistics are at the core of data science. A sturdy handle on statistics can help you extract more intelligence and obtain more meaningful results.
4. Programming
Some level of programming is required to execute a successful data science project. The most common programming languages are Python, and R. Python is especially popular because it’s easy to learn, and it supports multiple libraries for data science and ML.
5. Databases
A capable data scientist needs to understand how databases work, how to manage them, and how to extract data from them.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
A data scientist analyzes business data to extract meaningful insights. In other words, a data scientist solves business problems through a series of steps, including:
- Before tackling the data collection and analysis, the data scientist determines the problem by asking the right questions and gaining understanding.
- The data scientist then determines the correct set of variables and data sets.
- The data scientist gathers structured and unstructured data from many disparate sources—enterprise data, public data, etc.
- Once the data is collected, the data scientist processes the raw data and converts it into a format suitable for analysis. This involves cleaning and validating the data to guarantee uniformity, completeness, and accuracy.
- After the data has been rendered into a usable form, it’s fed into the analytic system—ML algorithm or a statistical model. This is where the data scientists analyze and identify patterns and trends.
- When the data has been completely rendered, the data scientist interprets the data to find opportunities and solutions.
- The data scientists finish the task by preparing the results and insights to share with the appropriate stakeholders and communicating the results.
Now we should be aware of some machine learning algorithms which are beneficial in understanding data science clearly.
Why Become a Data Scientist?
According to Glassdoor and Forbes, demand for data scientists will increase by 28 percent by 2026, which speaks of the profession’s durability and longevity, so if you want a secure career, data science offers you that chance.
Furthermore, the profession of data scientist came in second place in the Best Jobs in America for 2021 survey, with an average base salary of USD 127,500.
So, if you’re looking for an exciting career that offers stability and generous compensation, then look no further!
Where Do You Fit in Data Science?
Data science offers you the opportunity to focus on and specialize in one aspect of the field. Here’s a sample of different ways you can fit into this exciting, fast-growing field.
Data Scientist
- Job role: Determine what the problem is, what questions need answers, and where to find the data. Also, they mine, clean, and present the relevant data.
- Skills needed: Programming skills (SAS, R, Python), storytelling and data visualization, statistical and mathematical skills, knowledge of Hadoop, SQL, and Machine Learning.
Data Analyst
- Job role: Analysts bridge the gap between the data scientists and the business analysts, organizing and analyzing data to answer the questions the organization poses. They take the technical analyses and turn them into qualitative action items.
- Skills needed: Statistical and mathematical skills, programming skills (SAS, R, Python), plus experience in data wrangling and data visualization.
Data Engineer
- Job role: Data engineers focus on developing, deploying, managing, and optimizing the organization’s data infrastructure and data pipelines. Engineers support data scientists by helping to transfer and transform data for queries.
- Skills needed: NoSQL databases (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra DB), programming languages such as Java and Scala, and frameworks (Apache Hadoop).
Data Science Tools
The data science profession is challenging, but fortunately, there are plenty of tools available to help the data scientist succeed at their job.
- Data Analysis: SAS, Jupyter, R Studio, MATLAB, Excel, RapidMiner
- Data Warehousing: Informatica/ Talend, AWS Redshift
- Data Visualization: Jupyter, Tableau, Cognos, RAW
- Machine Learning: Spark MLib, Mahout, Azure ML studio
Difference Between Business Intelligence and Data Science
Business intelligence is a combination of the strategies and technologies used for the analysis of business data/information. Like data science, it can provide historical, current, and predictive views of business operations. However, there are some key differences.
| Business Intelligence | Data Science |
|---|---|
| Uses structured data | Uses both structured and unstructured data |
| Analytical in nature – provides a historical report of the data | Scientific in nature – perform an in-depth statistical analysis on the data |
| Use of basic statistics with emphasis on visualization (dashboards, reports) | Leverages more sophisticated statistical and predictive analysis and machine learning (ML) |
| Compares historical data to current data to identify trends | Combines historical and current data to predict future performance and outcomes |
Applications of Data Science

Data science has found its applications in almost every industry.
1. Healthcare
Healthcare companies are using data science to build sophisticated medical instruments to detect and cure diseases.
2. Gaming
Video and computer games are now being created with the help of data science and that has taken the gaming experience to the next level.
3. Image Recognition
Identifying patterns in images and detecting objects in an image is one of the most popular data science applications.
4. Recommendation Systems
Netflix and Amazon give movie and product recommendations based on what you like to watch, purchase, or browse on their platforms.
5. Logistics
Data Science is used by logistics companies to optimize routes to ensure faster delivery of products and increase operational efficiency.
6. Fraud Detection
Banking and financial institutions use data science and related algorithms to detect fraudulent transactions.
Data Science Use Cases
Here are some brief overviews of a couple of use cases, showing data science’s versatility.
- Law Enforcement: In this scenario, data science is used to help police in Belgium to better understand where and when to deploy personnel to prevent crime. With only limited resources and a large area to cover data science used dashboards and reports to increase the officers’ situational awareness, allowing a police force that’s spread thin to maintain order and anticipate criminal activity.
- Pandemic Fighting: The state of Rhode Island wanted to reopen schools, but was naturally cautious, considering the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The state used data science to expedite case investigations and contact tracing, enabling a small staff to handle an overwhelming number of concerned calls from citizens. This information helped the state set up a call center and coordinate preventative measures.
- Driverless Vehicles: Lunewave, a sensor manufacturing company, was looking for a way to make sensor technology more cost-effective and accurate. They turned to data science and machine learning to train their sensors to be safer and more reliable, as well as using data to improve their 3D-printed sensor manufacturing process.
FAQs
1. What’s the difference between data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning?
Artificial Intelligence makes a computer act/think like a human. Data science is an AI subset that deals with data methods, scientific analysis, and statistics, all used to gain insight and meaning from data. Machine learning is a subset of AI that teaches computers to learn things from provided data.
2. What is Data Science in simple words?
Data science is an AI subset that deals with data methods, scientific analysis, and statistics, all used to gain insight and meaning from data.
3. What does a Data Scientist do?
A data scientist analyzes business data to extract meaningful insights.
4. What is Data Science with an example?
Data science is the domain of study that deals with vast volumes of data using modern tools and techniques to find unseen patterns, derive meaningful information, and make business decisions. For example, finance companies can use a customer’s banking and bill-paying history to assess creditworthiness and loan risk.
5. What kinds of problems do data scientists solve?
Data scientists solve issues like:
- Loan risk mitigation
- Pandemic trajectories and contagion patterns
- Effectiveness of various types of online advertisement
- Resource allocation
- Do data scientists code?
A: Sometimes they may be called upon to do so.
6. Can I learn Data Science on my own?
A: Data science is a complex field with many difficult technical requirements. It’s not advisable to try learning data science without the help of a structured learning program.
Wrapping It All Up
Data will be the lifeblood of the business world for the foreseeable future. Knowledge is power, and data is actionable knowledge that can mean the difference between corporate success and failure. By incorporating data science techniques into their business, companies can now forecast future growth, predict potential problems, and devise informed strategies for success.
Do you have any questions regarding this ‘What is Data Science’ article? If so, then please put it in the comments section of the article.