In Spring, you can use @PropertySource annotation to externalize your configuration to a properties file. In this tutorial, we will show you how to use @PropertySource to read a properties file and display the values with @Value and Environment.
P.S @PropertySource has been available since Spring 3.1
1. @PropertySource and @Value
A classic example, read a properties file and display with ${}.
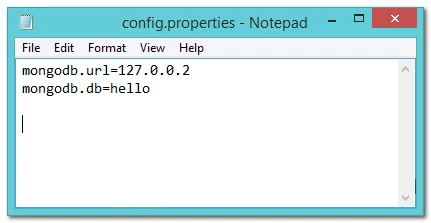
config.properties
mongodb.url=1.2.3.4
mongodb.db=helloAppConfigMongoDB
package com.favtuts.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
//...
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.favtuts.*" })
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties")
public class AppConfigMongoDB {
//1.2.3.4
@Value("${mongodb.url}")
private String mongodbUrl;
//hello
@Value("${mongodb.db}")
private String defaultDb;
@Bean
public MongoTemplate mongoTemplate() throws Exception {
MongoClientOptions mongoOptions =
new MongoClientOptions.Builder().maxWaitTime(1000 * 60 * 5).build();
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient(mongodbUrl, mongoOptions);
MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory = new SimpleMongoDbFactory(mongo, defaultDb);
return new MongoTemplate(mongoDbFactory);
}
//To resolve ${} in @Value
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigInDev() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
Note
To resolve ${} in
@Values, you must register a staticPropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurerin either XML or annotation configuration file.
2. @PropertySource and Environment
Spring recommends to use Environment to get the property values.
AppConfigMongoDB
package com.favtuts.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
//...
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.favtuts.*" })
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties")
public class AppConfigMongoDB {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
public MongoTemplate mongoTemplate() throws Exception {
String mongodbUrl = env.getProperty("mongodb.url");
String defaultDb = env.getProperty("mongodb.db");
MongoClientOptions mongoOptions =
new MongoClientOptions.Builder().maxWaitTime(1000 * 60 * 5).build();
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient(mongodbUrl, mongoOptions);
MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory = new SimpleMongoDbFactory(mongo, defaultDb);
return new MongoTemplate(mongoDbFactory);
}
}
3. More @PropertySource Examples
More common examples.
3.1 Example to resolve ${} within @PropertySource resource locations.
@Configuration
@PropertySource("file:${app.home}/app.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
Environment env;
}
Set a system property during startup.
System.setProperty("app.home", "test");
java -jar -Dapp.home="/home/mkyon/test" example.jar
3.2 Include multiple properties files.
@Configuration
@PropertySource({
"classpath:config.properties",
"classpath:db.properties" //if same key, this will 'win'
})
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
Environment env;
}
Note
If a property key is duplicated, the last declared file will ‘win’ and override.
4. Spring 4 and @PropertySources
Some enhancements on Spring 4.
4.1 Introduces new @PropertySources to support Java 8 and better way to include multiple properties files.
@Configuration
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties"),
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
})
public class AppConfig {
//...
}
4.2 Allow @PropertySource to ignore the not found properties file.
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:missing.properties")
public class AppConfig {
//...
}
If missing.properties is not found, the system is unable to start and throws FileNotFoundException
Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException:
class path resource [missiong.properties] cannot be opened because it does not existIn Spring 4, you can use ignoreResourceNotFound to ignore the not found properties file
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value="classpath:missing.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound=true)
public class AppConfig {
//...
}
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:missing.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound=true),
@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties")
})
Done.