This article shows you five examples to convert a string into a binary string representative or vice verse.
- Convert String to Binary –
Integer.toBinaryString - Convert String to Binary – Bit Masking
- Convert Binary to String –
Integer.parseInt - Convert Unicode String to Binary.
- Convert Binary to Unicode String.
1. Convert String to Binary – Integer.toBinaryString
The steps to convert a string to its binary format.
- Convert string to
char[]. - Loops the
char[]. Integer.toBinaryString(aChar)to convert chars to a binary string.String.formatto create padding if need.
StringToBinaryExample1.java
package com.favtuts.crypto.bytes;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class StringToBinaryExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "Hello";
String result = convertStringToBinary(input);
System.out.println(result);
// pretty print the binary format
System.out.println(prettyBinary(result, 8, " "));
}
public static String convertStringToBinary(String input) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
char[] chars = input.toCharArray();
for (char aChar : chars) {
result.append(
String.format("%8s", Integer.toBinaryString(aChar)) // char -> int, auto-cast
.replaceAll(" ", "0") // zero pads
);
}
return result.toString();
}
public static String prettyBinary(String binary, int blockSize, String separator) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
while (index < binary.length()) {
result.add(binary.substring(index, Math.min(index + blockSize, binary.length())));
index += blockSize;
}
return result.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(separator));
}
}
Output
0100100001100101011011000110110001101111
01001000 01100101 01101100 01101100 011011112. Convert String to Binary – Bit Masking.
2.1 This Java example will use bit masking technique to generate binary format from an 8-bit byte.
StringToBinaryExample2.java
package com.favtuts.crypto.bytes;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class StringToBinaryExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "a";
// String input = "Hello";
String result = convertByteArraysToBinary(input.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
System.out.println(prettyBinary(result, 8, " "));
}
public static String convertByteArraysToBinary(byte[] input) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : input) {
int val = b;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
result.append((val & 128) == 0 ? 0 : 1); // 128 = 1000 0000
val <<= 1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
public static String prettyBinary(String binary, int blockSize, String separator) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
while (index < binary.length()) {
result.add(binary.substring(index, Math.min(index + blockSize, binary.length())));
index += blockSize;
}
return result.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(separator));
}
}
Output
01100001The hard part is this code. The idea is similar to this Java – Convert Integer to Binary using bit masking. In Java, byte is an 8-bit, int is 32-bit, for integer 128 the binary is 1000 0000.
for (byte b : input) {
int val = b; // byte -> int
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
result.append((val & 128) == 0 ? 0 : 1); // 128 = 1000 0000
val <<= 1; // val = val << 1
}
}This & is an Bitwise AND operator, only 1 & 1 is 1, other combinations are all 0.
1 & 1 = 1
1 & 0 = 0
0 & 1 = 0
0 & 0 = 0This val <<= 1 is actually val = val << 1, it is a bit left shift operator, it moves the bits to the left side by 1 bit.
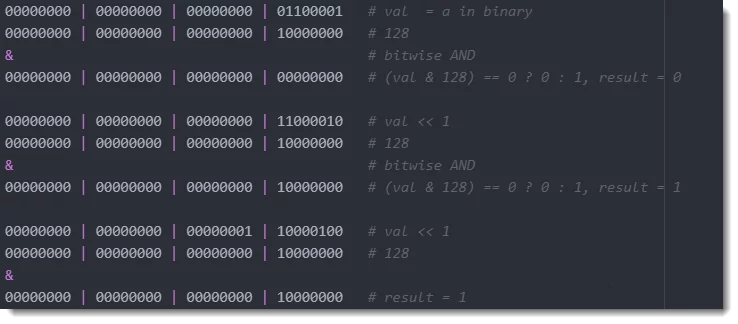
Review the following draft: let’s assume the val is an int, or byte represents a character a.
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 01100001 # val = a in binary
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
& # bitwise AND
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 # (val & 128) == 0 ? 0 : 1, result = 0
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 11000010 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
& # bitwise AND
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # (val & 128) == 0 ? 0 : 1, result = 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000001 | 10000100 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # result = 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000011 | 00001000 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 # result = 0
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000110 | 00010000 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 # result = 0
00000000 | 00000000 | 00001100 | 00100000 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 # result = 0
00000000 | 00000000 | 00011000 | 01000000 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 # result = 0
00000000 | 00000000 | 00110000 | 10000000 # val << 1
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # 128
&
00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 10000000 # result = 1
# collect all bits # 01100001For string a the binary string is 01100001.
3. Convert Binary to String.
In Java, we can use Integer.parseInt(str, 2) to convert a binary string to a string.
StringToBinaryExample3.java
package com.favtuts.crypto.bytes;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class StringToBinaryExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "01001000 01100101 01101100 01101100 01101111";
// Java 8 makes life easier
String raw = Arrays.stream(input.split(" "))
.map(binary -> Integer.parseInt(binary, 2))
.map(Character::toString)
.collect(Collectors.joining()); // cut the space
System.out.println(raw);
}
}
Output
Hello4. Convert Unicode String to Binary.
We can use Unicode to represent non-English characters since Java String supports Unicode, we can use the same bit masking technique to convert a Unicode string to a binary string.
This example converts a single Chinese character 你 (It means you in English) to a binary string.
UnicodeToBinary1.java
package com.favtuts.crypto.bytes;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class UnicodeToBinary1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] input = "你".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(input.length); // 3, 1 Chinese character = 3 bytes
String binary = convertByteArraysToBinary(input);
System.out.println(binary);
System.out.println(prettyBinary(binary, 8, " "));
}
public static String convertByteArraysToBinary(byte[] input) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : input) {
int val = b;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
result.append((val & 128) == 0 ? 0 : 1); // 128 = 1000 0000
val <<= 1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
public static String prettyBinary(String binary, int blockSize, String separator) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
while (index < binary.length()) {
result.add(binary.substring(index, Math.min(index + blockSize, binary.length())));
index += blockSize;
}
return result.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(separator));
}
}
Output
3
111001001011110110100000
11100100 10111101 10100000Different Unicode requires different bytes, and not all Chinese characters required 3 bytes of storage, some may need more or fewer bytes.
5. Convert Binary to Unicode String.
Read comments for self-explanatory.
UnicodeToBinary2.java
package com.favtuts.crypto.bytes;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class UnicodeToBinary2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String binary = "111001001011110110100000"; // 你, Chinese character
String result = binaryUnicodeToString(binary);
System.out.println(result.trim());
}
// <= 32bits = 4 bytes, int needs 4 bytes
public static String binaryUnicodeToString(String binary) {
byte[] array = ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(
Integer.parseInt(binary, 2)
).array();
return new String(array, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
}
Output
你Download Source Code
$ git clone https://github.com/favtuts/java-core-tutorials-examples
$ cd java-crypto