To successfully meet the challenges related to storing data in the cloud, Amazon provides a storage service to be used with your EC2 instances, called Amazon Elastic Block Storage or Amazon EBS. This service provides highly available block level storage volumes. In this what is AWS EBS in Amazon tutorial, you will get an in-depth understanding of AWS Amazon EBS Volume.
What is AWS EBS in Amazon?

Let me explain what is AWS EBS in laymen terms with the help of an example. Suppose, you have a system with 120GB of storage. You run out of space and you need more space, so you get an external disk and attach it to your system. Life is good, you are happy again. The Amazon EBS is equivalent to that external disk, with the only difference that it is supposed to be used with your EC2 instances (virtual systems) on AWS cloud.
Now let’s understand what is AWS EBS Volume in technical terms.
Although Amazon does offer local storage for every EC2 Instance that you can use while you run the instance but as soon as the instance is shut down, the data in that local storage is also lost. Therefore, if you need to save the data, you would need Amazon EBS with your EC2 instance.
Since we have already understood what EBS is, in Laymen terms, let’s now focus on more technical definition of Amazon EBS.
AWS EBS is largely defined as a raw block level storage service, designed to be used with Amazon EC2 instances. Each block acts like a hard drive, where any type of file can be stored or even a whole operating system can be installed on it. Each EBS volume that you attach with your EC2 instance is automatically replicated within its availability zone to prevent data loss and component failure. With EBS, one can easily scale their usage up or down in a matter of few minutes.
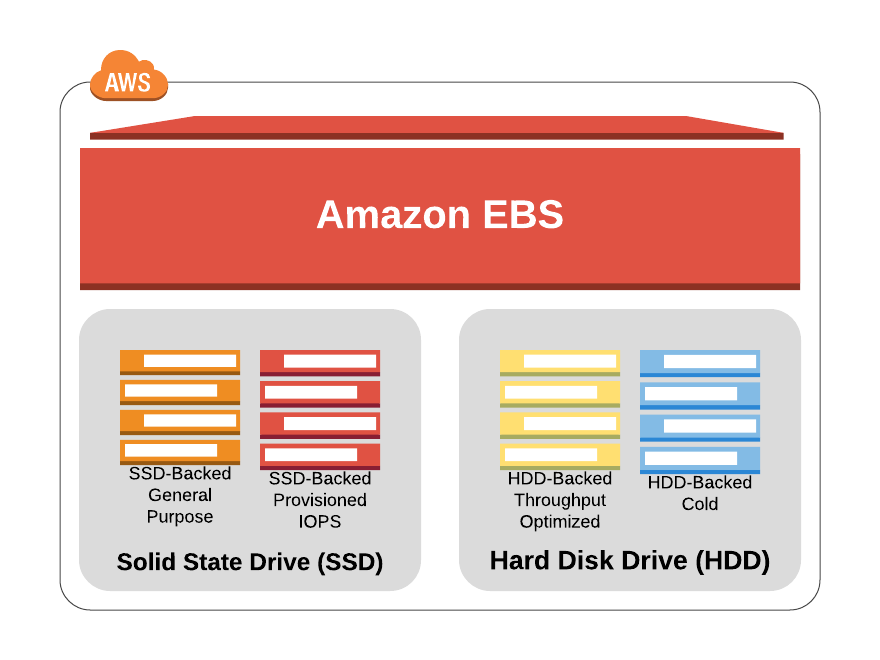
Types of Amazon Elastic Block Store
AWS provides different EBS volume options for different workloads and use cases. All these different EBS volumes are either backed up by SSD (Solid-state drive) or a hard disk drive (HDD).
- SSD (Solid-state drive): SSD backed EBS Volumes are optimized specially for transactional workloads where the volume is supposed to perform a lot of small read and write operations.
- HDD (Hard disk drive): HDD backed volumes are specifically designed for large workloads.
Following are different types of EBS Volumes that fall under the category if SDD backed and HDD backed EBS Volumes.
General Purpose SSD is recommended for most of the use cases as it is suitable for small and medium workloads such as frequently accessing workloads, applications in development and production environments, system boot volumes and more. SSD supports 3 IOPS (input Output Operations per second) per GB. The volume size for this volume is 1 GiB – 16 TiB.
Provisioned IOPS SSD are usually used for critical production applications and databases that require high performance EBS storage. This type of EBS volume is designed to be suitable for the most demanding I/O workloads. The Volume size for this volume is 4 GiB – 16 TiB.
Throughput Optimized HDD EBS Volumes are designed for applications that require large storage as well as large throughput and where IOPS is not relevant. Such as big data warehousing, log processing and more. The volume size for this volume is 500 GiB – 16 TiB.
Cold HDD is designed for less frequently accessed workloads This volume is a magnetic storage format which is suitable for cases where storing data at low cost is usually the main criteria. The volume size in this volume is 500GiB – 16 TiB.
Features of AWS EBS
Amazon EBS Snapshots
EBS Snapshot, as defined by Amazon Web Services, is a Point in time, incremental copy of the Amazon EBS volume.
Snapshots contain all the information needed to restore your data from in EBS volumes. Being incremental backup of the data means when the snapshot is taken for the first time on an EBS volume, all the block data will be captured, and then in the next snapshot, it only captures the block changes since the last snapshot (provided that the first snapshot still exists while taking the second snapshot).
All the snapshots taken of a block are chained together. When an EBS snapshot is used to restore the data, the data particular to that EBS snapshot is restored as well as the data from the previous snapshots.
What you can and cannot do with EBS Snapshot?
| Can do | Cannot do |
| A snapshot can be copied to another region, or to your own AWS account. | A snapshot cannot be accessed directly |
| A snapshot can be shared with another account. | A snapshot cannot be copied outside AWS |
| A snapshot can be used to create a whole fresh EBS Volume | A snapshot cannot be used to restore data into or onto an existing EBS Volume |
Availability and durability
Amazon has made sure to provide high availability and durability for all their services and EBS is no different in this aspect. At no extra charges, Amazon replicates the EBS Volume data across multiple servers in an availability zone so as to prevent the loss of data.
The annual failure rate (AFR) of EBS volumes falls between 0.1% – 0.2% which makes it approximately 20 times more reliable than typical commodity disk drives. The annual failure rate of traditional disk drives is around 4%.
EBS Encryption
AWS also offers seamless data encryption for EBS Volumes.
When an encrypted EBS Volume is attached to an instance then all the data, including data on the volume, disk I/O and even the snapshots created from that encrypted volume, are all encrypted. This feature eliminates the need to structure and manage a secure key management infrastructure. EBS encryption occurs at the servers that host EC2 instances. EBS encryption offers data security using Amazon managed keys or the keys that the users create themselves using AWS key management Service (KMS).
Moving on with this what is AWS EBS tutorial, let’s look into the benefits of AWS Elastic Block Store.
Benefits of AWS EBS

Reliability: To prevent component failures, EBS Volume can automatically respond to its respective availability Zone.
Secure: There are various access control policies that Amazon provides which can be used to specify who can access which EBS Volumes.
Flexibility: EBS Volumes can be scaled up and down as required and they support live configuration changes. Modifications such as volume type, volume size and IOPS capacity without any service interruptions
Easy Data Backup: Data backup can be easily taken by taking point in time snapshots of Amazon EBS volumes that are stored redundantly in multiple availability zones. Taking a snapshot does not depend whether the EBS Volume is connected to any instance or not.
Properties of Amazon Elastic Block Store
- An EBS Volume can only be assigned to a single EC2 instance at a time.
- Volumes other than the root volumes can be encrypted but the root volume cannot be encrypted without using any of their party tools
- The root volumes are deleted by default when the EC2 instance is terminated.
- The size of an EBS volume can go up to 16 TiB.
- The copy of screenshots can be created between AWS regions so as to create volumes in different regions.
Hope this what is AWS EBS tutorial helps
Watch this AWS Services video